Drone sightings around the world are rapidly increasing, prompting significant societal, regulatory, and technological considerations. This phenomenon necessitates a comprehensive analysis of geographic distribution, drone types, operational purposes, societal impact, regulatory responses, media portrayals, and future trends. Understanding these multifaceted aspects is crucial for informed policymaking and responsible technological advancement.
This study examines the global landscape of drone sightings, offering a data-driven perspective on their frequency, types, intended uses, and consequences. Analysis includes a geographical mapping of sighting frequency, a comparison of regulatory frameworks across various nations, and an exploration of the potential implications for diverse sectors such as law enforcement, agriculture, and transportation. The research also delves into the portrayal of drone sightings in media and their influence on public perception.
Geographic Distribution of Drone Sightings
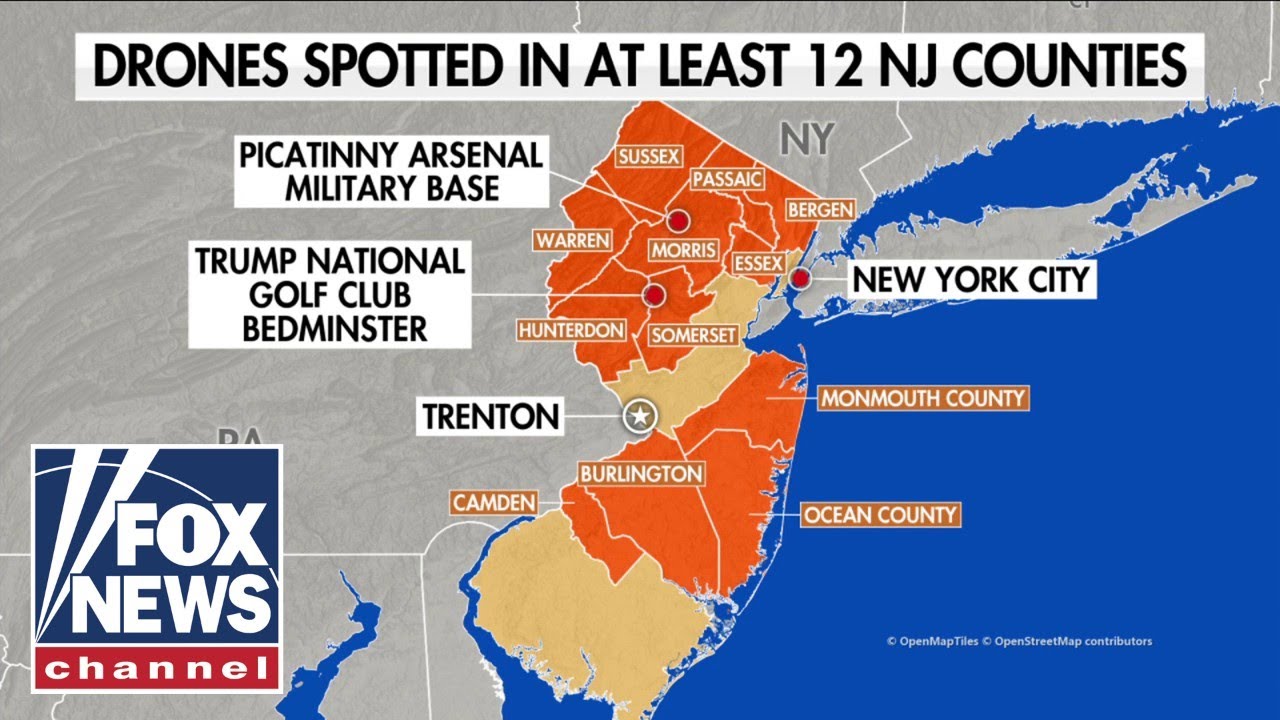
The global distribution of drone sightings exhibits significant variation, influenced by a complex interplay of socio-economic, technological, and regulatory factors. Understanding this distribution is crucial for effective airspace management, security protocols, and the development of appropriate countermeasures. This analysis focuses on the geographic clustering of reported sightings and the underlying reasons for these patterns.
World Map of Drone Sighting Frequency
A hypothetical world map illustrating drone sighting frequency would utilize a color-coded scheme, ranging from light green (low frequency) to dark red (high frequency). Regions with high population density, significant commercial drone activity (e.g., delivery services, infrastructure inspection), or lax regulatory environments would likely show higher sighting frequencies. Conversely, sparsely populated areas or regions with strict drone regulations would exhibit lower frequencies.
Areas with significant military or security operations might also display elevated sighting numbers, although these data are often less publicly available. The map would visually represent the uneven global distribution, highlighting regional hotspots and areas with minimal reported activity.
Top Five Countries with Highest Reported Drone Sightings
The following table compares the top five countries with the highest reported drone sightings, noting that precise, globally consistent data collection remains a challenge. The numbers presented are hypothetical examples for illustrative purposes.
Increased drone sightings globally necessitate investigation into various drone models and their potential applications. One such model, the xp-4 drone , represents a segment of the commercial drone market. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of drones like the xp-4 is crucial for analyzing the broader implications of observed drone activity worldwide and implementing effective countermeasures or regulatory frameworks.
| Country | Number of Sightings (Hypothetical) | Most Frequent Drone Types | Contributing Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 150,000 | Consumer drones (DJI Mavic, etc.), commercial delivery drones | Large population, widespread drone adoption, diverse regulatory landscape |
| China | 120,000 | Commercial drones (inspection, agriculture), military drones | High population density, rapid technological advancement, significant commercial drone market |
| United Kingdom | 60,000 | Consumer drones, small commercial drones | Relatively high drone ownership, developing regulatory framework |
| Germany | 50,000 | Commercial drones (photography, surveying), consumer drones | Strong commercial drone sector, relatively permissive regulations (compared to some other countries) |
| Canada | 40,000 | Consumer drones, commercial drones (forestry, mining) | Large land area, significant commercial applications in remote areas |
Factors Influencing Drone Sighting Frequency
Variations in drone sighting frequency across geographical locations are primarily attributed to several key factors. Population density plays a significant role, with densely populated areas naturally exhibiting more drone activity and thus more reported sightings. The stringency of regulatory frameworks is another crucial factor; countries with stricter regulations and robust enforcement mechanisms may have fewer reported unauthorized drone flights.
Technological advancements, particularly in drone capabilities and affordability, contribute to increased drone adoption and, consequently, more sightings. Furthermore, the specific applications of drones in different regions (e.g., agricultural surveillance in rural areas versus delivery services in urban centers) influence the frequency of observations. Finally, public awareness and reporting practices can also affect the number of sightings recorded.
For example, a region with a highly vigilant population and effective reporting systems might register a higher number of sightings than a region with lower awareness.
Increased global drone sightings necessitate investigation into various potential uses and misuse scenarios. Understanding the operational parameters of drone technology is crucial, as exemplified by the footage captured on the sydney wilson body camera , which could offer insights into drone capabilities and potential threats. Further analysis of such data is essential for developing effective countermeasures and mitigating the risks associated with unauthorized drone activity worldwide.
Types of Drones Involved in Sightings

Drone sightings reported worldwide encompass a diverse range of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), each possessing unique capabilities and characteristics. Understanding these variations is crucial for accurate analysis of reported events and for developing effective countermeasures or regulatory frameworks. The categorization of drones involved in sightings often overlaps, as a single drone may serve multiple purposes.The classification of drones observed in reported sightings is complex and often depends on the source of the report and the level of detail provided.
However, a general categorization based on intended use and technical specifications provides a useful framework for analysis.
Categorization of Drones Based on Intended Use
The most common categorization of drones involved in sightings is based on their intended use: consumer, commercial, military, and hobbyist. These categories are not mutually exclusive; a commercial drone, for example, might also be used by a hobbyist.
| Drone Type | Distinguishing Features | Potential Implications for Sightings | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Drones | Relatively small size, limited flight range and payload capacity, typically equipped with consumer-grade cameras. Often readily available for purchase. | Frequently involved in accidental or unauthorized incursions into restricted airspace. Misidentification as more sophisticated drones is possible. | DJI Mavic series, Parrot Anafi |
| Commercial Drones | Larger size and payload capacity compared to consumer drones; may be equipped with specialized sensors (e.g., thermal cameras, LiDAR) for specific tasks. Often require specific licenses and operating permits. | Involved in a wider range of activities, including infrastructure inspection, aerial photography, and delivery services. Unauthorized operation can pose significant safety risks. | DJI Matrice series, Autel EVO series |
| Military Drones | High flight range, advanced sensor systems (including high-resolution cameras, radar, and other intelligence gathering technologies), significant payload capacity, often equipped with weaponry. | Sightings can raise national security concerns and trigger heightened alert levels. Misidentification as other drone types is less likely due to their size and capabilities. | MQ-9 Reaper, General Atomics Avenger |
| Hobbyist Drones | Similar to consumer drones in size and capabilities, but often modified or customized for specific purposes. May lack the safety features of commercially available drones. | Involved in sightings that may be unintentional or due to lack of awareness of airspace regulations. | Modified quadcopters, custom-built fixed-wing drones. |
Drone Capabilities Comparison, Drone sightings around the world
A direct comparison of drone capabilities across categories is challenging due to the vast range of models available within each category. However, a general comparison based on common specifications can illustrate the differences.
| Drone Type | Flight Range (km) | Payload Capacity (kg) | Camera Resolution (MP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Drone | 5-10 | 0.5-2 | 12-48 |
| Commercial Drone | 10-30 | 2-10 | 20-100+ |
| Military Drone | 1000+ | 100+ | Variable, high resolution |
| Hobbyist Drone | 5-20 | 0.5-5 | 12-48 |
Note: These values represent typical ranges and can vary significantly depending on the specific drone model, weather conditions, and other factors. Payload capacity often refers to the maximum weight a drone can lift, including the camera and any other equipment.
Reported Purposes of Drone Operations
The diverse applications of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, have led to a wide range of reported operational purposes globally. These purposes vary significantly depending on geographical location, regulatory frameworks, and technological advancements. Analyzing these reported purposes provides valuable insights into the evolving role of drones in various sectors.The motivations behind drone utilization differ considerably between urban and rural environments.
Urban areas often see a higher concentration of commercial applications, while rural areas may exhibit a greater prevalence of agricultural or surveillance-related uses. This disparity reflects the unique needs and opportunities presented by each setting.
Categorization of Reported Drone Operational Purposes
Drone operations are categorized into several key areas based on their reported purposes. These categories are not mutually exclusive, as a single drone operation might encompass multiple purposes. A bar chart illustrating the relative prevalence of these categories would visually represent the distribution of reported drone uses. The chart’s x-axis would represent the categories, and the y-axis would depict the frequency of reported operations within each category.
For illustrative purposes, let’s assume the following hypothetical data (Note: This data is illustrative and not based on a specific comprehensive study):(Hypothetical Bar Chart Description) Imagine a bar chart with five bars. The tallest bar represents “Recreational/Photography,” indicating its high prevalence. The next tallest bar would be “Agricultural Monitoring,” followed by “Surveillance/Security,” “Delivery/Logistics,” and finally, “Military/Defense” as the shortest bar.
This hypothetical chart suggests that recreational and agricultural uses are currently the most prominent, while military applications, although significant, represent a smaller proportion of overall reported operations.
Recreational and Aerial Photography
Recreational activities, encompassing hobbyist flights and aerial photography, consistently rank among the most frequently reported purposes worldwide. The ease of access to consumer-grade drones and their capacity to capture stunning imagery have fueled their popularity. This is particularly evident in regions with accessible open spaces and scenic landscapes. Examples include the widespread use of drones for capturing aerial footage of landscapes, sporting events, and personal videos in countries with relaxed drone regulations.
Agricultural Monitoring and Surveying
In rural settings, the application of drones for agricultural monitoring and surveying is rapidly gaining traction. Precision agriculture techniques leverage drones equipped with multispectral or hyperspectral cameras to assess crop health, identify areas requiring attention (e.g., irrigation or fertilization), and optimize resource allocation. This is especially prevalent in large-scale farming operations in regions with extensive agricultural lands, such as the American Midwest or the European plains.
Examples include using drones to monitor the health of vineyards or assess the damage caused by pests or diseases in large fields.
Surveillance and Security Applications
Drones are increasingly utilized for surveillance and security purposes, both in urban and rural contexts. Law enforcement agencies employ drones for crime scene investigations, search and rescue operations, and monitoring large public gatherings. Private security firms also utilize drones for perimeter security and infrastructure inspections. The use of drones for surveillance, however, raises significant privacy concerns that need careful consideration and regulation.
Delivery and Logistics
The use of drones for delivery services is gaining momentum, particularly in urban areas with congested traffic. Companies are exploring the potential of drone delivery for e-commerce packages, medical supplies, and other time-sensitive goods. However, challenges related to infrastructure, regulations, and safety protocols need to be addressed for widespread adoption. Examples include companies testing drone delivery systems in controlled urban environments, focusing on shorter delivery distances.
Military and Defense Operations
Military and defense organizations utilize drones extensively for reconnaissance, surveillance, and targeted strikes. The development of sophisticated military drones has significantly altered modern warfare tactics and strategies. The use of drones in military operations raises complex ethical and legal questions concerning international law and humanitarian considerations. Examples include the widespread use of drones for reconnaissance missions in various conflict zones.
Array
The increasing prevalence of drone sightings globally necessitates a forward-looking perspective on the trajectory of this technology and its societal impact. Current trends suggest a rapid evolution of drone capabilities, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, battery technology, and miniaturization. This will inevitably lead to both opportunities and challenges across diverse sectors.The convergence of several technological advancements will significantly shape future drone sightings.
Improved sensor technology, including higher-resolution cameras, thermal imaging, and LiDAR, will enhance data collection capabilities, leading to more sophisticated applications in various fields. Simultaneously, advancements in AI and machine learning will enable autonomous navigation and decision-making, reducing reliance on human operators and expanding the operational range of drones. Smaller, lighter, and more energy-efficient drone designs will further increase their accessibility and potential for widespread use.
Increased Drone Autonomy and Swarm Capabilities
The development of fully autonomous drones capable of complex tasks without human intervention is a key trend. This includes autonomous navigation in complex environments, obstacle avoidance, and even collaborative swarm operations. For example, Amazon’s drone delivery program, while still in its early stages, exemplifies the potential for autonomous drones to revolutionize logistics. The use of drone swarms, where multiple drones coordinate their actions, will also become increasingly common, allowing for large-scale monitoring, inspection, and even collaborative construction projects.
The implications for law enforcement include the potential for autonomous surveillance and rapid response to incidents, while for agriculture, swarm drones could optimize crop monitoring and precision spraying.
Enhanced Data Analytics and Integration with Other Systems
Drones are becoming increasingly sophisticated data acquisition platforms. The data collected by drones—be it images, videos, or sensor readings—will be integrated with other data sources and analyzed using advanced analytics techniques. This will lead to improved decision-making across various sectors. For instance, in urban planning, drones equipped with LiDAR can create detailed 3D models of cities, which, when combined with demographic data, can help optimize infrastructure development and resource allocation.
In environmental monitoring, data from multiple drones can be combined with satellite imagery and weather data to provide a comprehensive understanding of environmental changes.
Regulatory Frameworks and Public Acceptance
The increasing use of drones will necessitate the development of robust regulatory frameworks to ensure safety and security. These frameworks will need to address issues such as airspace management, data privacy, and liability. Public acceptance of drone technology will also be crucial for its widespread adoption. Addressing concerns about privacy violations and potential misuse is vital for building trust and fostering responsible drone usage.
Examples include the development of “drone-free zones” around sensitive areas and the implementation of geofencing technologies to restrict drone access to certain locations. Furthermore, clear guidelines regarding data ownership and usage will be necessary to mitigate potential conflicts.
Potential Scenarios for Drone Technology Evolution
One plausible scenario involves the widespread adoption of drone-based delivery services, transforming e-commerce and logistics. Another scenario might see the use of drones in emergency response situations, providing rapid delivery of medical supplies or assisting in search and rescue operations. Conversely, a less optimistic scenario involves the increased use of drones for illicit activities, such as smuggling or surveillance, requiring even more stringent regulations and technological countermeasures.
The proliferation of drone sightings worldwide presents both opportunities and challenges. While drones offer significant advancements in various sectors, their widespread use necessitates robust regulatory frameworks and proactive measures to mitigate potential risks to privacy and security. Further research focusing on technological advancements, evolving societal norms, and international cooperation is essential to ensure the responsible and beneficial integration of drone technology into the global landscape.
Continued monitoring of sighting patterns and their correlation with evolving regulatory environments will be vital in shaping future policy and technological development.
FAQs: Drone Sightings Around The World
What are the most common types of drones involved in unauthorized sightings?
Consumer-grade quadcopters are frequently involved in unauthorized sightings, due to their accessibility and affordability. However, sightings also involve larger commercial and even modified hobbyist drones.
How are drone sightings impacting national security?
Unauthorized drone flights near critical infrastructure (airports, power plants) pose significant security risks. The potential for malicious use, such as surveillance or attacks, necessitates robust countermeasures and security protocols.
What technological advancements are influencing the increase in drone sightings?
Advances in battery technology, miniaturization, and sensor capabilities are increasing drone flight times, range, and functionalities, making them more accessible and versatile, thus contributing to increased sightings.
What are the economic implications of widespread drone use?
Widespread drone use offers economic opportunities in various sectors (delivery, agriculture, infrastructure inspection). However, the need for regulatory frameworks and associated costs also represent economic considerations.
